Here are some notes that I took on Mitosis and Meiosis
A chromosome is just
coiled up DNA
S
phase of Replication of DNA
Replicates
the other side of the chromosome
Sister Chromatids
are connected by Centromere
Split the sister
chromatids to get two single chromatids
Mitosis
Interphase
G1
Growth
Normal living
S
Protein Synthesis
DNA Replication
G2
Getting ready to mitosis
(M)
Mitotic Phase
Mitosis
Split the Chromosome into two
Cytokinesis
Splitting of the cells into two separate
cells
Checkpoints
Basically…
When
checkpoint is down, it is like a green light
When
checkpoint is up, it is like a red light
Controlling
Mitosis
Caused
by fluctuation between MPF activity and the enzyme Cyclin
Eukaryote
Process
by which the contents of the eukaryotic nucleus are separated into two
genetically identical packages
Start
with sister chromatids in a cell nucleus
Interphase
Prophase
The
nuclear envelope disintegrates
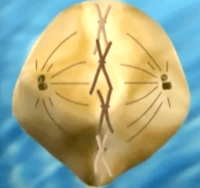
Metaphase
Sister
Chromatids move toward the center
Then
they attach their centromeres to spindle fibers
Anaphase
The
Sister Chromatids split into single chromosomes
Pac-man...eat
away at the spindle fibers which causes movements
Telephase
Nuclear
envelope forms each set of chromosomes
Prokaryote
No nucleus --> no mitosis
Binary
Fission
Meiosis
At
the start, each chromosome finds its homologous counterpart
Crossing
over occurs.
Spindles
pull the homologs apart. Sister Chromatids are not split
Repeat.
Creates
four cells. Each with one copy of each chromosome.

.jpg)






.png)
.png)